
We can also calculate the actual yield and theoretical yield if the percent yield is given. Percent yield is either less than 100% or greater. We use a formula to find the value of the percent yield. Percent yield is obtained by calculating the results of the division of actual yield and the theoretical yield. Thus, the actual yield in the given experiment is 75.0g. If the percent yield in the experiment is 15% and the chemical reaction has a theoretical yield of 5g, calculate the actual yield of the chemical reaction. Thus, the actual yield in the given experiment is 40.25g. SolutionĪctual yield = % yield x theoretical yield / 100 If the percent yield in the experiment is 115% and the chemical reaction has a theoretical yield of 35g, calculate the actual yield of the chemical reaction.

As per the percent yield formula, percent yield is equals to the actual yield, divided by theoretical yield and multiphy by 100. Thus, the Theoretical yield in the given experiment is 69.23g. The percentage yield calculator uses percent yield formula to show results. If the percent yield in the experiment is 65% and the chemical reaction has an actual yield of 45g, calculate the theoretical yield of the chemical reaction. Thus, the Theoretical yield in the given experiment is 14.29g. Theoretical yield = (actual yield/ percent yield) x 100 If the percent yield in the experiment is 105% and the chemical reaction has an actual yield of 15g, calculate the theoretical yield of the chemical reaction. Theoretical yield = (actual yield/ percent yield) x 100%Īctual yield = % yield x theoretical yield / 100 Examples to evaluate the theoretical yield. We can calculate accurate results of the percent yield, actual yield, and theoretical yield by using the percent yield calculator.
#Percent yield chemistry calculator how to#
How to calculate the actual yield and theoretical yield if the percent yield is given?īy modifying the formula of percent yield, we can also calculate the actual yield and theoretical yield if the percent yield is given. Thus, the percent yield in the given experiment is 78.9%. Step 3: Put the values in the above formula. Percent yield = % yield = (actual yield/ theoretical yield) x 100% In a chemical reaction of an experiment, the actual yield is 5g and the theoretical yield is 6.34g, compute the percent yield. Since the value of actual yield is usually less than the theoretical yield, the percentage yield is always less than 100%.Thus, the percent yield in the given experiment is 102.9%. Percentage yield of NaCl = 8.50 grams ÷ 9.93 grams × 100% Let’s assume that you obtained an actual yield of 8.50 grams. Percentage yield = mass of actual yield ÷ mass of theoretical yield × 100% The formula for calculating the percent yield is: Based on that value, you can find the percentage yield by using the ratio of the actual yield and the theoretical yield. If you actually carry out this reaction in a lab, you will be able to find the actual yield of the reaction. Theoretical yield of NaCl in grams = 9.93 grams Step 5: Find the Percentage Yield Theoretical yield of NaCl in grams = 0.17 moles of NaCl × 58.44 g/mole Theoretical yield of NaCl in grams = theoretical yield in moles × molar mass of NaCl We can convert the value from moles to grams by multiplying it with the molar mass of NaCl, which is equal to 58.44 g/mole. In the given problem, we need to find out how many grams of NaCl would be produced in the reaction. Therefore, the theoretical yield of NaCl in moles is 0.17 moles.īut this value is in terms of moles. We have found that Na is the limiting reagent in the reaction, and that for 0.17 moles of Na, 0.17 moles of NaCl are produced. Therefore, Na is the limiting reagent in this reaction, as it would produce lesser number of moles, if it were used up fully in the reaction.
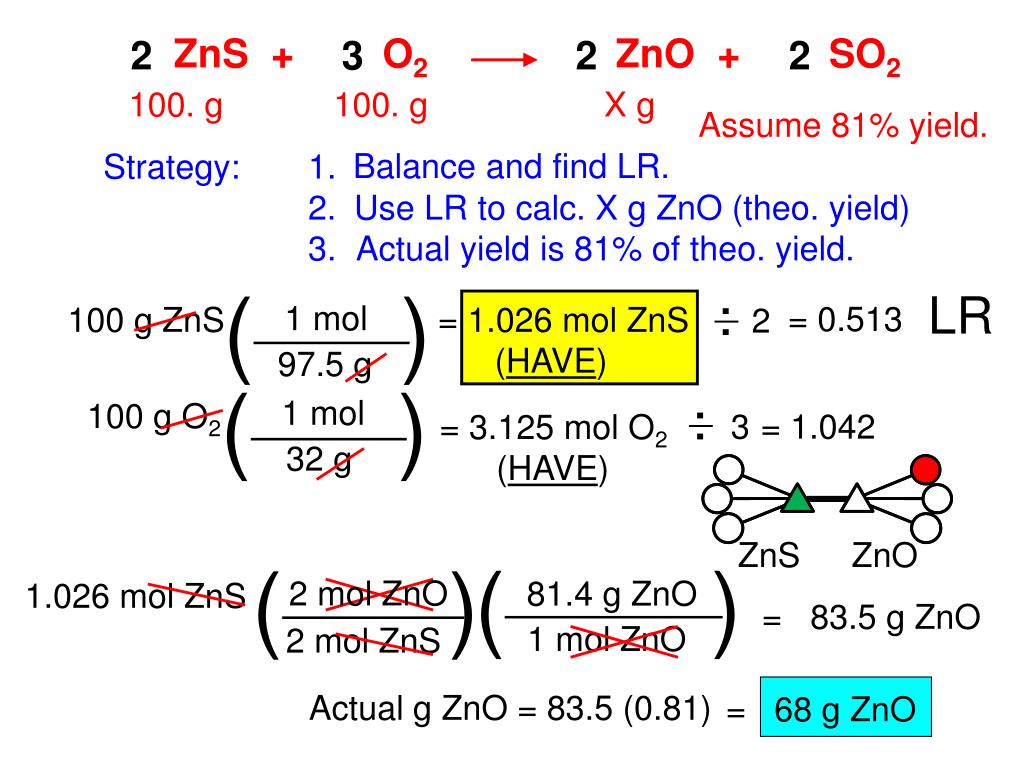
Therefore, for one mole of Cl 2, you will get 2 moles of NaCl.įor 0.21 moles of Cl 2, you will end up with 0.42 moles of NaCl. The stoichiometric coefficients of Cl 2 is 1 and that of NaCl is 2. Therefore, for one mole of Na, you will get 1 mole of NaCl.įor 0.17 moles of Na, you will end up with 0.17 moles of NaCl. In the balanced equation given above, the stoichiometric coefficient of both Na and NaCl is 2. How much product would Cl 2 produce, if it were used up completely in the reaction?.

How much product would Na produce, if it were used up completely in the reaction?.Now, the next step is to determine which of the two reactants is the limiting reagent. Number of moles of Cl 2 = 0.21 moles of Cl 2 Step 3: Find the Limiting Reagent Number of moles of Cl 2 = 15 grams ÷ 70.90 g/mole Number of moles of Na = 4 grams ÷ 22.99 g/mole Number of moles of Na = amount of Na in the reaction (in grams) ÷ molar mass of Na Number of moles of a substance = mass of the reactant ÷ molar mass of the reactant


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
